On the local network it does ARP scan.
-sL, List Scan, is a reverse DNS scan
Shows dns names and descovers the IP of a domain from the record on the DNS server
nmap facebook.com/24 -sL
List all dns names in the range that belongs the domain, ex: nmap external.edafomichaniki.gr/24 -sL
Reverse DNS Check options
List scan… reverse DNS scan: is the querying technique of the Domain Name System (DNS) to determine the domain name associated with an IP address – the reverse of the usual “forward” DNS lookup of an IP address from a domain name. The process of reverse resolving of an IP address uses PTR records. rDNS involves searching domain name registry and registrar tables. The reverse DNS database of the Internet is rooted in the .arpa top-level domain.
Examples
sudo nmap facebook.com/24 -sL Reverse DNS Check based on DNS Server – Check Network names.nmap 192.168.1.1-50 -sL --dns-server 192.168.1.1
nmap -sL 192.168.1.0/24 — list every address in that subnet with reverse-DNS names.-iR, Random host scan
Check random number of hosts – Random Targets, Random with List Scan
Nmap -iR 300 -sL -vv //random 300 clients
Nmap -iR 3 -vv
-sn, Check host ping without Port scan
- Not port scan detected from firewall.
- Check also if host is UP. With no discovery options, sends:
- list all up hosts in the local network and MAC and IP
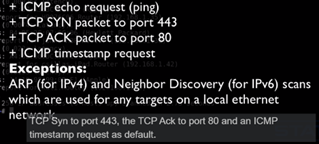
nmap -sn means “Ping Scan” (sometimes called host discovery). It tells Nmap: check which hosts are up, but don’t scan any ports.
What it does
- Sends ICMP echo requests (ping).
- Sends TCP SYN to port 443 and TCP ACK to port 80 by default (to detect live hosts even if ICMP is blocked).
- Marks hosts as up or down.
- Useful to map out which IPs in a range are active without doing intrusive port scans.
- It does not scan ports for services (no open ports info).
- It does not list every IP like
-sLdoes. - It only shows hosts that respond as alive.
Examples
sudo nmap -sn chrisjanel.eu
Output:
Starting Nmap 7.95 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-09-29 04:26 EDT
Nmap scan report for chrisjanel.eu (46.226.193.12)
Host is up (0.0046s latency).
rDNS record for 46.226.193.12: hermes.dnhost.net
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.53 seconds-Pn, Disable host discovery, Treat all host like are up
Executes the default scan (1000 first ports, ICMP, etc) and treats all host like are up.
Treat all hosts as online — skip host discovery (ping phase).
What normally happens without -Pn
- By default, Nmap first does host discovery (ping sweep) to check if a host is “up” before scanning ports.
- If a host doesn’t respond (e.g., ICMP blocked by a firewall), Nmap will skip scanning it.
With -Pn
Nmap does not ping. It assumes the target is alive and goes straight to port scanning. This is useful if:
- Firewalls block ICMP or TCP ping probes.
- You want to force Nmap to scan even “silent” hosts
Notes & Cautions
- Using
-Pncan slow scans a lot on large ranges, because Nmap will try ports on every single IP (even offline ones). - It may generate more noise in IDS/IPS logs.
- For large ranges, it’s better to combine host discovery (
-sn) first, then scan alive hosts.
Examples
nmap -Pn 192.168.1.10
→ Scan all default ports of that IP, even if it doesn’t reply to ping.
nmap -Pn -p 22,80,443 192.168.1.0/24
→ Scan ports 22, 80, and 443 on the entire subnet, without host discovery.
sudo nmap -sS -Pn example.com
→ Do a SYN scan, skipping host discovery.
PS/PA/PU/PY[portlist]: TCP SYN/ACK, UDP or SCTP discovery to given ports
PS: Send SYN packets to specific ports. TCP SYN. If port is closed, not expecting anything just get reset. If port is open, continues with TCP handshake but nmap ignore it and act like reset. Doesn’t care if the port is open or closed.
Then continues with the default port scan… continues with other ports.
nmap -iR 10 -PS[22-25,80,113,1050] -v
nmap 192.68.1.1-10 -PS[22-25,80,113,1050] -v
Does the same but after the selected ports does not do port scan
nmap 192.68.1.1-10 -PS[22-25,80,113,1050] -sn -v
PA: send an ACK for the discovery
nmap 192.68.1.1-10 -PA[22-25,80,113,1050] -sn -v
PU: For UDP discovery.
Example: search for DNS servers with UDP discovery
nmap -iR 10 -PU53 -sn -vv
PS:
nmap -PS873 -sn emoh.dyndns.info -vv
Host is up, received syn-ack ttl 56 (0.097s latency).
rDNS record for 77.49.177.199: 199.177.49.77.in-addr.arpa
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 6.00 seconds
Raw packets sent: 1 (44B) | Rcvd: 1 (44B)nmap -PS874 -sn emoh.dyndns.info -vv
Note: Host seems down. If it is really up, but blocking our ping probes, try -Pn
Nmap done: 1 IP address (0 hosts up) scanned in 2.60 seconds
Raw packets sent: 2 (88B) | Rcvd: 0 (0B)-PE: ICMP EchoScanning local network if Hosts is UP and show Mac address – Local Network scan
nmap 192.168.1.1-255 -PE -sn -vv
-PO [protocol list]: IP Protocol Ping – Local Network scan
nmap 192.168.1.1-20 -PO1 -sn
-PR: Arp scan instead of IP scan – Fastest Local Network scan, Fast scan of local network with MAC and manufacture
Host is up, received arp-response (0.028s latency).
MAC Address: 10:FE:ED:C7:23:71 (TP-Link Technologies)
nmap 192.168.1.1-1/24 -PR -sn -vv
Port state scan
nmap -p 80,443,873 emoh.dyndns.info -vv